In this article, you will learn how to implement routing in React JS. We will develop the following functionalities:
- Create multiple React components.
- Add routes to each component.
- Allow users to navigate between different pages.
1. Install react-router-dom npm package
React is a JavaScript library, not a framework hence many of the functionalities including routing aren’t built-in and need to be added through npm packages.
We will install the “react-router-dom” package to add routing functionality to the project. With the terminal command below:
npm i react-router-dom
// For projects configured with yarn
yarn add react-router-domOnce the package is successfully installed, we can verify the dependencies from the package.json of the project.

2. Create React Components for home, about and blog
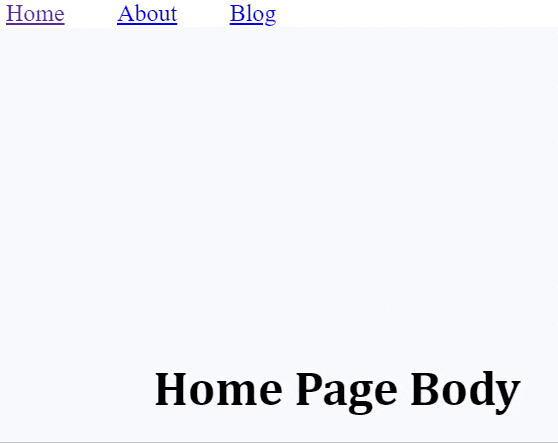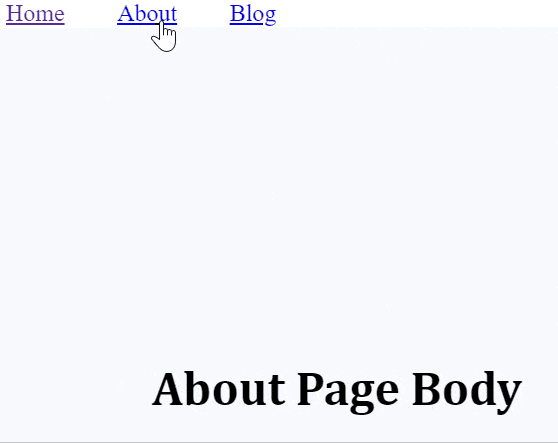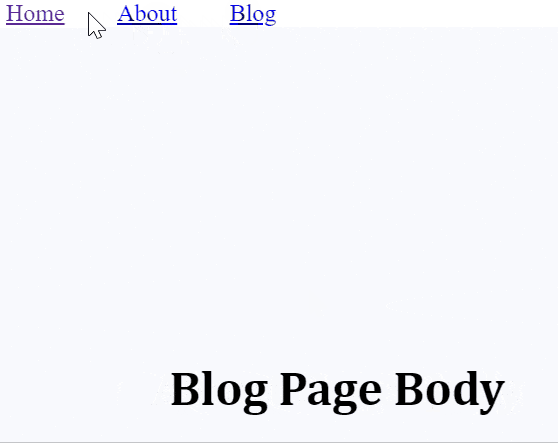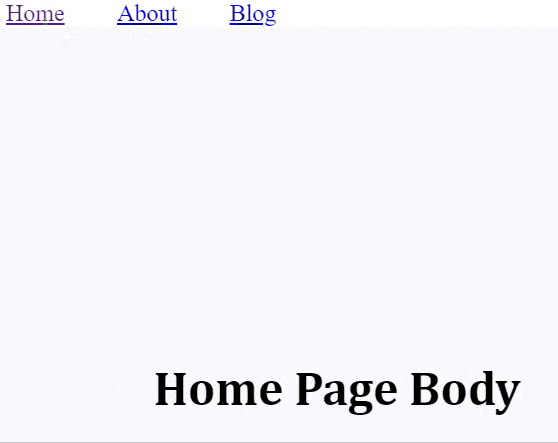
We will create a React component for the Home page which displays a heading with the text “Home Page Body“.
import React from "react";
//Homepage Component
function Home() {
return (
<div className="app">
<h1>Home Page Body</h1>
</div>
);
}
export default Home;Similarly, two other components for the About and blog page is created.
3. Wrap App componenent with <Switch/> and <Router/>
To configure the routes, all the required components are imported from “react-router-dom” package. We enclose the whole App component in <Router/> which enables all the functionality of “react-router-dom” within it.
Further, <Switch/> renders the first route that matches the current browser URL.
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Switch, Route, Link } from "react-router-dom";
const App = () => (
<Router>
<Switch>
</Switch>
</Router>
);
const rootElement = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App />, rootElement);4. Declare Routes for the components
Now we need to configure routes for every component using the <Route/> tag. The <Route/> tag accepts the path of the route and renders the component wrapped around it. Ie, <Home/> component is rendered for exact path “/“, <About/> component is rendered for any path starting with “/about“, etc.
// Import components
import Home from "./Home";
import About from "./About";
import Blog from "./Blog";
const App = () => (
<Router>
<Switch>
{/* Exact match to avoid
overriding other routes */}
<Route path="/" exact>
<Home />
</Route>
<Route path="/about">
<About />
</Route>
<Route path="/blog">
<Blog />
</Route>
</Switch>
</Router>
);5. Add links for all the routes
Once Routes are configured, the required component is rendered based on the browser URL. However, to allows users to switch between components by click, we will add <Link/> tag. When users click on the text enclosed by <Link/>, the browser directs to the URL provided in the to attribute.
<div className="nav-bar">
<Link to="/"> Home </Link>
<Link to="/about"> About </Link>
<Link to="/blog"> Blog </Link>
</div>Final Solution Code
App.js
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Switch, Route, Link } from "react-router-dom";
// Import components
import Home from "./Home";
import About from "./About";
import Blog from "./Blog";
import "./styles.css";
const App = () => (
<Router>
<div className="nav-bar">
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
<Link to="/about">About</Link>
<Link to="/blog">Blog</Link>
</div>
<Switch>
{/* Exact match to avoid
overriding other routes */}
<Route path="/" exact>
<Home />
</Route>
<Route path="/about">
<About />
</Route>
<Route path="/blog">
<Blog />
</Route>
</Switch>
</Router>
);
const rootElement = document.getElementById("root");
ReactDOM.render(<App />, rootElement);Home.js
import React from "react";
//Homepage Component
function Home() {
return (
<div className="app">
<h1>Home Page Body</h1>
</div>
);
}
export default Home;About.js
import React from "react";
//About Component
const About = () => {
return (
<div className="app">
<h1>About Page Body</h1>
</div>
);
};
export default About;Blog.js
import React from "react";
//Blog Component
function Blog() {
return (
<div className="app">
<h1>Blog Page Body</h1>
</div>
);
}
export default Blog;styles.css
.app {
font-family: sans-serif;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
flex-direction: column;
gap: 20px;
height: 100vh;
font-family: Cambria, Cochin, Georgia, Times, "Times New Roman", serif;
background-color: #f8f9fd;
}
.nav-bar {
display: flex;
gap: 35px;
font-size: 18px;
padding: 20px;
}